Summary of our research
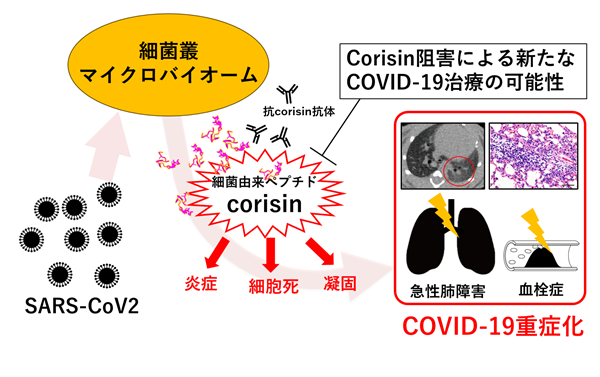
SARS-CoV-2, the deadly new virus that causes COVID-19, can be fatal due to acute lung injury (ALI) and blood clots in severe cases. Scientists have suspected that the microbiota, the bacteria living in our bodies, may influence how bad COVID-19 gets, but they did not know the exact mechanism. Now, a breakthrough study by immunologists from Mie University has uncovered a shocking link: corisin, a peptide released by the microbiota, is present at elevated levels in the blood of COVID-19 patients and is associated with blood coagulation activation. What is more, they showed that blocking corisin in mice with lung damage caused by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein improved their health. This is the first time in the world that anyone has shown that a microbiota-derived peptide can cause lung injury and blood coagulation activation in COVID-19, opening up new possibilities for treating this deadly disease with anti-corisin drugs. The stunning results were published online in the Journal of Thrombosis and Haematosis, the prestigious journal of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, on March 5th, 2024.
Researcher information

Taro Yasuma
Assistant Professor, Department of Diabetes & Endocrinology/ Department of Immunology, Mie University Graduate School of Medicine
Specialized area:
Diabetes and Endocrinology, Immunology
Current research field:
microbiome, diabetes, organ fibrosis

Gabazza Esteban
Professor, Mie University Graduate School of Medicine
Specialized area:
Immunology, Respiratory Medicine
Current research field:
respiratory disease, coagulation and fibrinolysis, microbiome